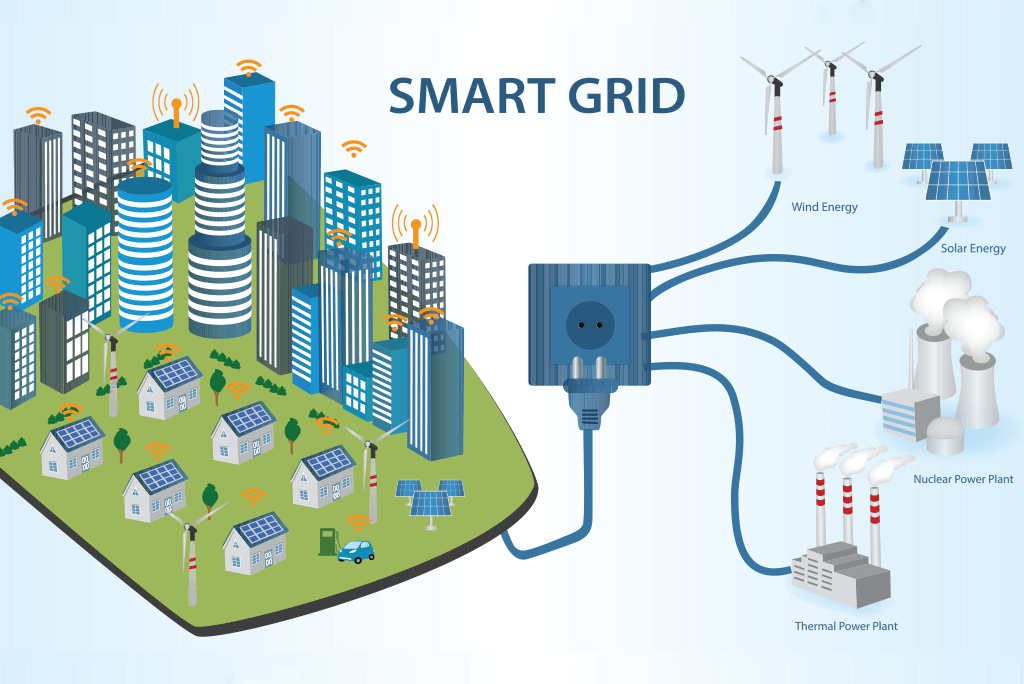
With urban and industrial areas being digitized, next-generation sensors are becoming the building blocks of smart infrastructure. Next-generation sensors facilitate real-time sensing of data, monitoring, and automation and are redefining city and industrial network operations.
From energy-efficient buildings to intelligent transport systems, sensors are revolutionizing infrastructure efficiency, safety, and sustainability.
The Role of Sensors in Smart Infrastructure
Even more brilliant infrastructure is fueled by data-driven decision making and its strongest fuel source: sensors.
Advanced sensors are able to track and detect temperature, humidity, vibration, air quality, and traffic volume and provide critical feedback to maximize performance and minimize downtime. Installed in roads, bridges, or grids, these technologies provide predictive maintenance to keep systems reliable and safe.
For instance, IoT-based environment sensors track the level of pollution in urban areas and structural health monitoring sensors track the stability of buildings and bridges. In the same way, smart water meters and smart energy meters provide utmost usage of resources and sustainability with a decrease in operational costs.
Technologies Enabling Next-Generation Sensors
Technological advancements in edge computing, artificial intelligence (AI), and machine learning (ML) are the reason behind the development of sensors. AI-based sensors can compute at the edge and hence support decision-making at a high rate without cloud connectivity in real time. Such an ability is needed by timeliness-critical applications such as traffic management, public safety, and emergency response.
Apart from that, 5G connectivity speeds up the efficiency of the smart infrastructure by effortless sharing of data among control systems, sensors, and devices.
Large-scale deployment is made economically viable and feasible by using sensor networks with low power to create fully connected cities.
Benefits and Future Outlook
Third-generation sensors allow governments, corporations, and developers to build intelligent, adaptive, and green infrastructure. They are able to forecast failures prior to occurrence, minimize upkeep expenses, and promote the safety of residents.
With data forming the basis of infrastructure development, the scope of smart sensors keeps growing, pushing innovation in sectors like building construction, energy, and transport.
Conclusion
Smart infrastructure in the future is founded on convergence of innovative sensor technology. Cities and businesses can build networked, effective, and sustainable environments with next-generation sensors that redefine operational excellence and living in the contemporary world.
